Peripheral Neuropathy
Tired of the burning, tingling, crawling sensations, or electric pains in your hands and feet? Already tried “everything” without success? Don’t give up! The Nerve & Disc Institute has helped lots of patients end peripheral neuropathy pain and get their life back.
You are not alone.
Thousands of patients just like you have found success at The Nerve & Disc Institute when all other treatments failed. Contact us to see if you qualify for treatment
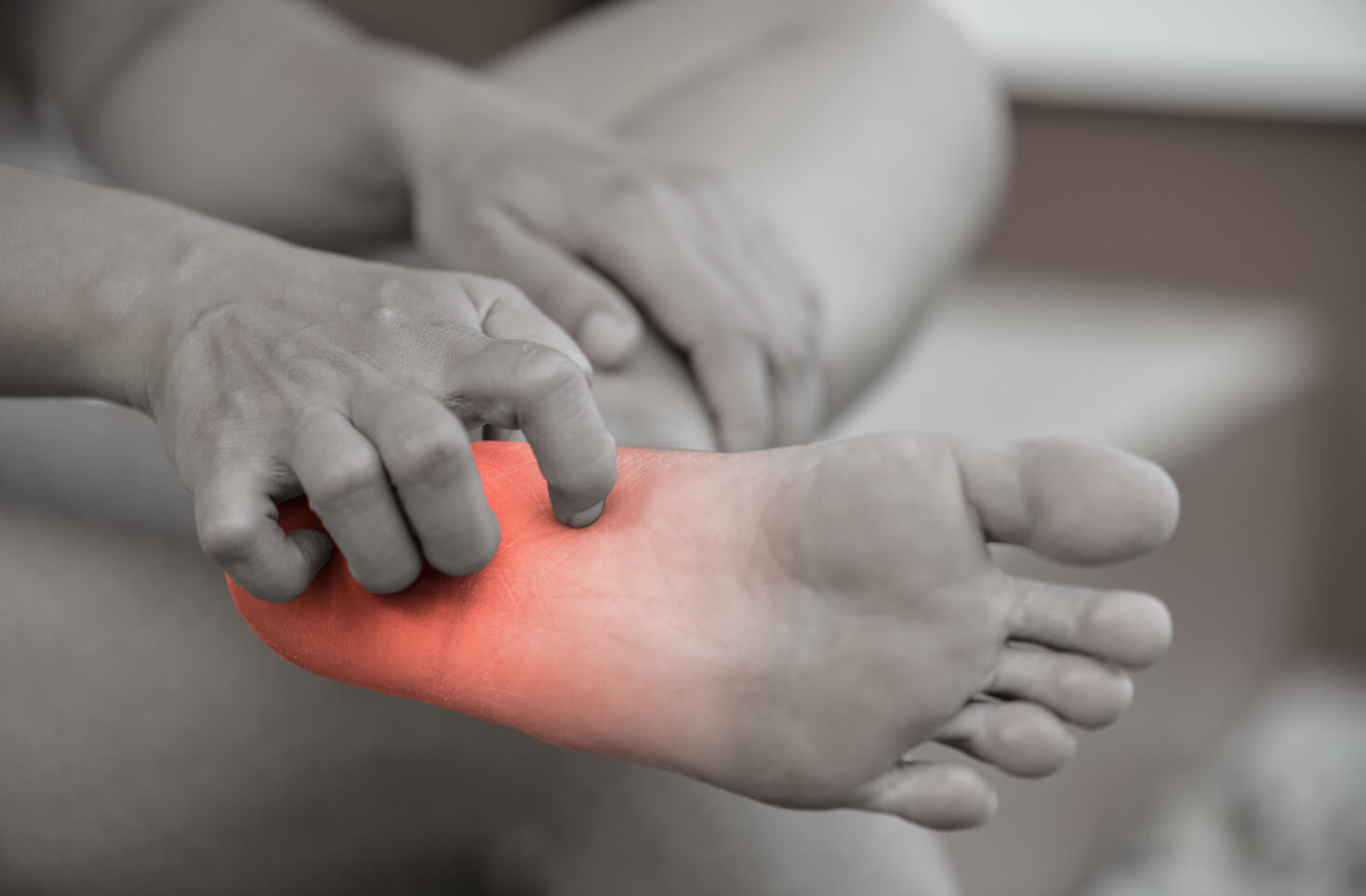
Symptoms
- Tingling or numbness
- Feels like something is in your shoe but there’s not
- Abnormal sensations
- Feels like you have socks on, even though you are barefoot
- It is becoming harder and harder to walk
- Losing your balance more often
- Stumble into things
- Unbearable foot pain
- Feels like pins and needles
- Restless legs
- No longer can feel hot or cold sensations
- Spontaneous pinching, sharpness, or electric shocks
Many of our patients have tried any and all treatments available before coming to The Nerve & Disc Institute. Some have found temporary relief with medications or other short term solutions while others have found no relief at all. If you are one of those suffering in pain and have tried other medical options only to have them fail, don’t give up hope. You deserve to live without the excruciating pain or discomfort of neuropathy.
Patient Recovery Stories & Reviews
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is a collection of disorders that occurs when nerves of the peripheral nervous system (the part of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord) are damaged. The condition is generally referred to as peripheral neuropathy, and it is most commonly due to damage to nerve axons. Neuropathy usually causes pain and numbness in the hands and feet. It can result from traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic disorders, and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes of neuropathy is diabetes.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a common form of neuropathy. Over time, uncontrolled sugar levels can damage your nerves. This nerve damage causes different symptoms and the problems first appear in the toes, feet, and hands. The custom treatment program available from The Nerve & Disc Institute has delivered success in a large number of our patients where other treatments or facilities have failed.
Neuropathy can affect nerves that control muscle movement (motor nerves) and those that detect sensations such as coldness or pain (sensory nerves). In some cases – autonomic neuropathy – it can affect internal organs, such as the heart, blood vessels, bladder, or intestines.
Pain from peripheral neuropathy is often described as a tingling or burning sensation. There is no specific length of time that the pain exists, but symptoms often improve with time – especially if the neuropathy has an underlying condition that can be cured. The condition is often associated with poor nutrition, a number of diseases, and pressure or trauma, but many cases have no known reason (called idiopathic neuropathy).
What Causes Peripheral Neuropathy
About 30% of neuropathy cases are considered idiopathic, which means they are of unknown cause. Another 30% of neuropathies are due to diabetes. In fact, about 50% of people with diabetes develop some type of neuropathy. The remaining cases of neuropathy, called acquired neuropathies, have several possible causes, including:
• Trauma or pressure on nerves, often from a cast or crutch or repetitive motion such as typing on a keyboard
• Nutritional problems and vitamin deficiencies, often from a lack of B vitamins
• Alcoholism, often through poor dietary habits and vitamin deficiencies
• Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barre syndrome
• Tumors, which often press up against nerves
• Other diseases and infections, such as kidney disease, liver disease, Lyme disease, HIV/AIDS, or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
• Inherited disorders (hereditary neuropathies), such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and amyloid polyneuropathy
• Poison exposure, from toxins such as heavy metals, and certain medications and cancer treatments
Treatments we offer
Therapeutic options such as the ReBuilder, laser therapy, vibration therapy, and dietary supplementation stand out as hopeful choices for individuals looking for alleviation
Addressing peripheral neuropathy effectively involves a holistic strategy that targets the root causes as well as the symptoms. Our methods concentrate on improving nerve functionality, diminishing inflammation, and bolstering nerve health overall, presenting an opportunity for enhanced movement and enriched life quality for those suffering from neuropathy. With ongoing advancements in research, the horizon for groundbreaking treatments offering enduring relief continues to expand, signifying considerable progress in the management of neuropathy.

